Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Microwave Photonics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
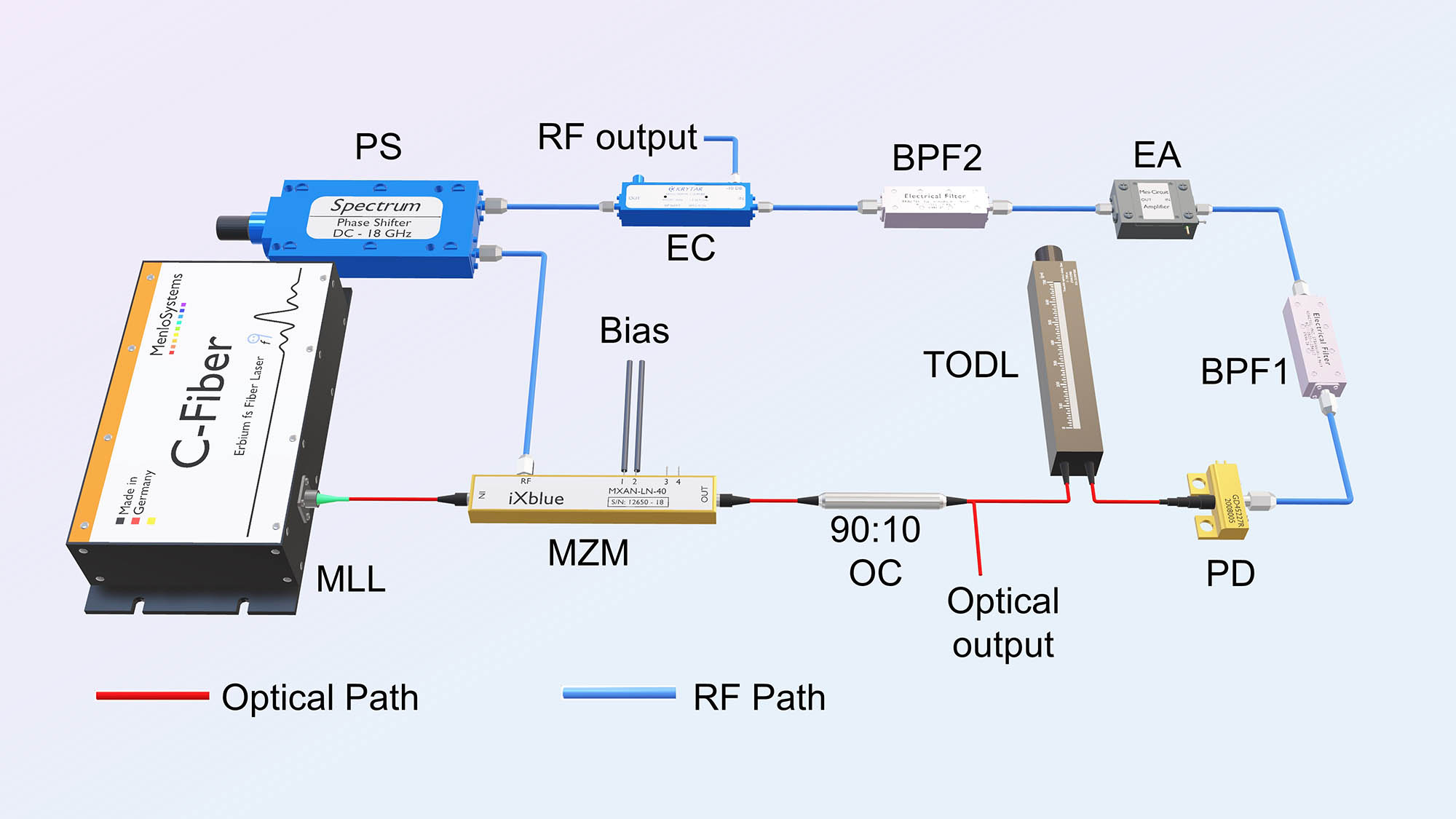
An approach for frequency division of an optical pulse train (OPT) based on an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. When the OPT is injected into the OEO, a microwave signal with a frequency equaling fractional multiples of the repetition rate of the OPT is generated. This signal is then fed back to the OEO, maintaining its oscillation, while simultaneously serving as the control signal of a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) in the OEO. The MZM acts as an optical switch, permitting specific pulses to pass through while blocking others. As a result, the repetition rate of the OPT is manipulated. A proof-of-concept experiment is carried out. Frequency division factors of 2 and 3 are successfully achieved. The phase noises of the OPT before and after the frequency division are investigated. Compared to previously reported systems, no external microwave source and sophisticated synchronization structure are needed.
frequency division optoelectronic oscillator mode-locked laser microwave photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043902

Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Microwave Photonics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
High accuracy and time resolution optical transfer delay (OTD) measurement is highly desired in many multi-path applications, such as optical true-time-delay-based array systems and distributed optical sensors. However, the time resolution is usually limited by the frequency range of the probe signal in frequency-multiplexed OTD measurement techniques. Here, we proposed a time-resolution enhanced OTD measurement method based on incoherent optical frequency domain reflectometry (I-OFDR), where an adaptive filter is designed to suppress the spectral leakage from other paths to break the resolution limitation. A weighted least square (WLS) cost function is first established, and then an iteration approach is used to minimize the cost function. Finally, the appropriate filter parameter is obtained according to the convergence results. In a proof-of-concept experiment, the time-domain response of two optical links with a length difference of 900 ps is successfully estimated by applying a probe signal with a bandwidth of 400 MHz. The time resolution is improved by 2.78 times compared to the theoretical resolution limit of the inverse discrete Fourier transform (iDFT) algorithm. In addition, the OTD measurement error is below . The proposed algorithm provides a novel way to improve the measurement resolution without applying a probe signal with a large bandwidth, avoiding measurement errors induced by the dispersion effect.
optical transfer delay measurement time resolution enhancement incoherent OFDR adaptive filtering Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(1): 013901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
2 United Microelectronics Center, Chongqing, 40030, China
3 School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui 230009, China
There has been a rapidly growing demand for low-cost, integrated single-shot spectrometers to be embedded in portable intelligent devices. Even though significant progress has been made in this area, two major problems are still remaining, namely the high temperature sensitivity and poor bandwidth-resolution ratio (BRR) that can’t meet the requirement of most applications. In this work, we present an integrated single-shot spectrometer relying on a silicon photonic circuit that has a footprint less than 3mm2, but could achieve broad operation bandwidth about 100 nm and high resolution up to 0.1 nm (with a BRR ~ 1000). Moreover, for the first time, we demonstrate an integrated spectrometer that could operate within a wide temperature range (between 10 and 70 degrees Celsius) without additional power consumption for temperature management.
1 微波毫米波单片集成和模块电路重点实验室,南京2006
2 南京电子器件研究所,南京10016
3 南京航空航天大学 电子信息工程学院,南京211106
4 空军装备部上海局,上海200231
基于硅基铌酸锂薄膜(Lithium Niobate on insulator,LNOI)材料平台,设计并制备了高速电光开关芯片,并实现了芯片的光纤耦合、管壳封装和性能测试。测试结果表明,该高速电光开关器件的开关速度达到13.4 ns,消光比达到31.8 dB。研究工作对未来研制光学延时芯片和波束形成网络芯片具有重要的支撑意义。
铌酸锂薄膜 电光开关 光学波束形成 LNOI electro-optic switch optical beamforming
1 南京航空航天大学 电子信息工程学院, 雷达成像与微波光子技术教育部重点实验室, 南京 211106
2 苏州大学 光电科学与工程学院, 教育部现代光学技术重点实验室, 江苏 苏州 215006
由于具有动力学特性丰富、体积小和易集成等优点, 基于半导体激光器的信号产生技术已成为高性能微波光子信号产生的优选方案之一。半导体激光器在合适的外光注入条件下能够工作在单周期振荡态, 可突破本征弛豫振荡频率的限制, 产生频率大范围可调的微波信号; 进一步动态地控制注入参数, 能够生成宽带可重构的微波调频信号, 在雷达领域具有重要的应用前景。文章首先介绍了基于光注入半导体激光器的宽带微波信号生成机理并实验产生了大时宽带宽积的微波线性调频信号, 其中心频率、带宽、时宽和工作频段均可灵活调谐; 然后, 构建了延时匹配光电反馈环路, 提升了宽带微波调频信号的频谱纯度和梳齿信噪比等性能参数; 最后, 基于该高性能宽带微波调频信号发生器构建了微波光子雷达验证系统, 分析了其在目标探测与成像方面的性能。
半导体激光器 微波光子学 光注入 线性调频信号 雷达 semiconductor laser microwave photonics optical injection linear frequency-modulated signal radar

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
2 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
A broadband instantaneous multi-frequency measurement system based on chirped pulse compression, which potentially has a sub-megahertz (MHz) accuracy and a hundred-gigahertz (GHz) measurement range, is demonstrated. A signal-under-test (SUT) is converted into a carrier-suppressed double-sideband (CS-DSB) signal, which is then combined with an optical linearly frequency-modulated signal having the sweeping range covering the +1st-order sideband of the CS-DSB signal. With photodetection, low-pass filtering, and pulse compression, accurate frequencies of the SUT are obtained via locating the correlation peaks. In the experiment, single- and multi-frequency measurements with a measurement range from 3 to 18 GHz and a measurement accuracy of <±100 MHz are achieved.
instantaneous frequency measurement chirped pulse compression frequency-to-time mapping microwave photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(10): 101202
红外与激光工程
2021, 50(7): 20211048
红外与激光工程
2021, 50(7): 20211056
南京航空航天大学 电子信息工程学院 雷达成像与微波光子技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 南京 211106
微波光子雷达利用光子学方法实现雷达信号的产生与处理,具有突出的宽带工作能力,能显著提升雷达距离分辨率。为了提升雷达角度分辨能力并实现灵活波束控制,将微波光子雷达技术与阵列技术相结合是必然的发展趋势。目前研究较多的宽带阵列雷达采用光真延时技术克服宽带波束倾斜问题,通常面临复杂度高、灵活性差、延时精度有限等问题。近年来,基于微波光子倍频与去斜接收的宽带雷达收发架构得到了广泛关注,基于此技术构建的阵列雷达,在实现宽带工作的同时具备实时数字补偿与处理功能,为宽带阵列雷达的发展提供了新的思路。文中针对作者在此方面的最新研究进展进行了综述,在阐明基于微波光子倍频与去斜接收实现宽带雷达收发机理的基础上,介绍了构建宽带相控阵雷达的方法以及实现数字波束扫描与成像的性能。然后,将阵列形式扩展至多输入多输出(MIMO)形式,介绍了基于光波分复用技术实现宽带微波光子MIMO雷达的方法,并分析了微波光子MIMO雷达在目标探测与成像方面的性能。
微波光子学 雷达 相控阵 MIMO 波束成形 microwave photonics radar phased array MIMO beamforming 红外与激光工程
2021, 50(7): 20211051
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
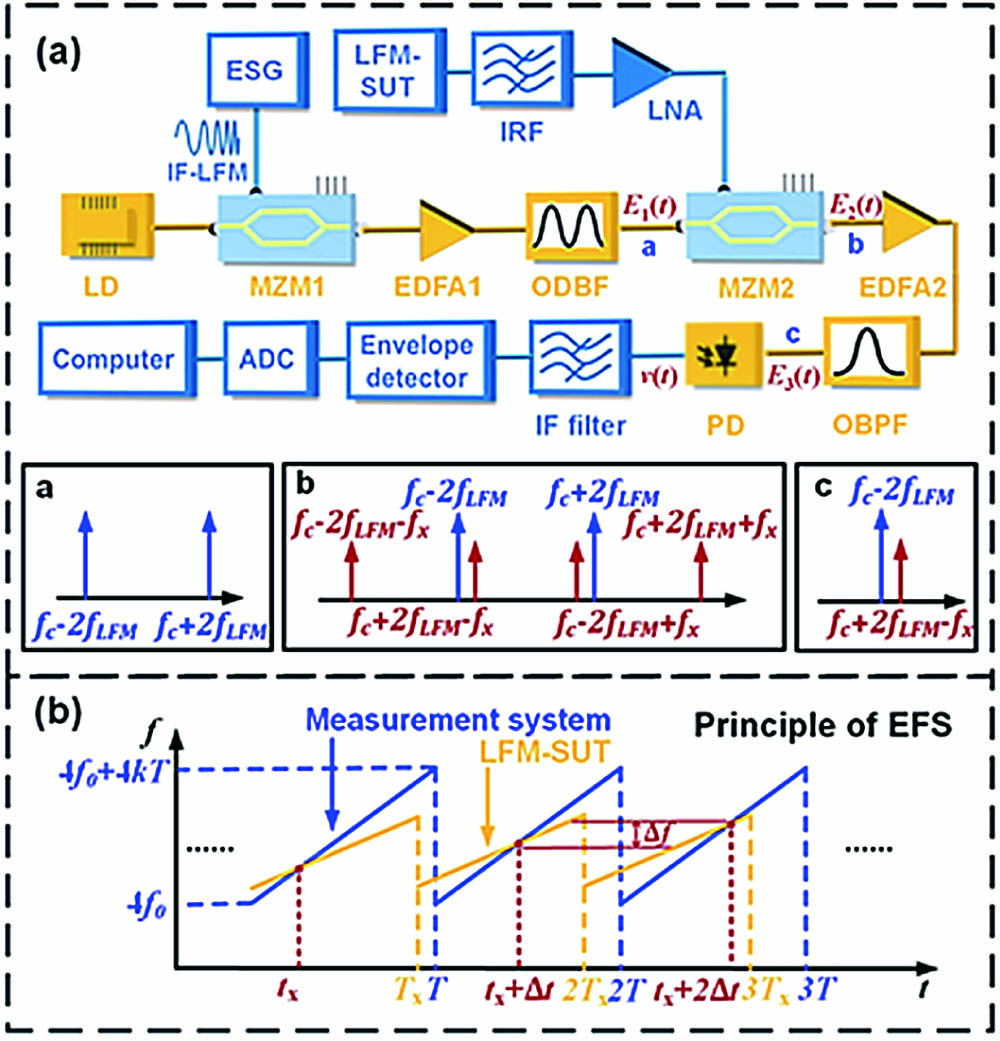
We propose a photonics-assisted equivalent frequency sampling (EFS) method to analyze the instantaneous frequency of broadband linearly frequency modulated (LFM) microwave signals. The proposed EFS method is implemented by a photonic scanning receiver, which is operated with a frequency scanning rate slightly different from the repetition rate of the LFM signals. Compared with the broadband LFM signal analysis based on temporal sampling, the proposed method avoids the use of high-speed analog to digital converters, and the instantaneous frequency acquisition realized by frequency-to-time mapping is also simplified since real-time Fourier transformation is not required. Feasibility of the proposed method is verified through an experiment, in which frequency analysis of -band LFM signals with a bandwidth up to 3 GHz is demonstrated with a moderate sampling rate of 100 MSa/s. The proposed method is highly demanded for analyzing the instantaneous frequency of broadband LFM signals used in radar and electronic warfare systems.
frequency measurement equivalent frequency sampling microwave photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(1): 013901





